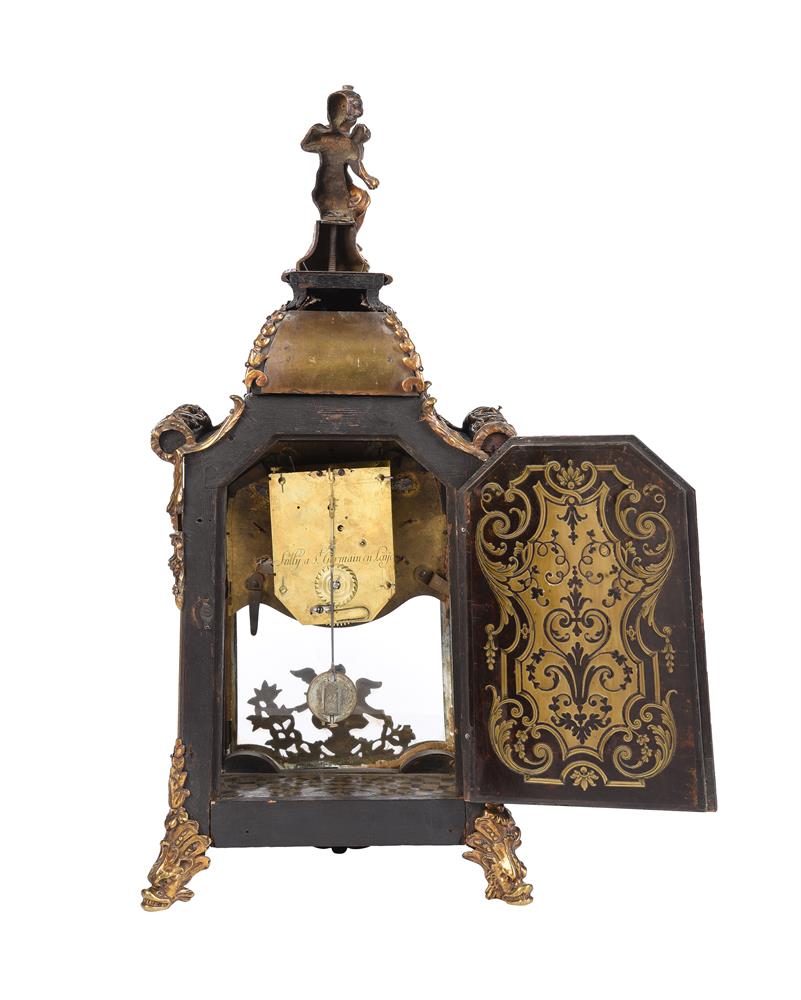
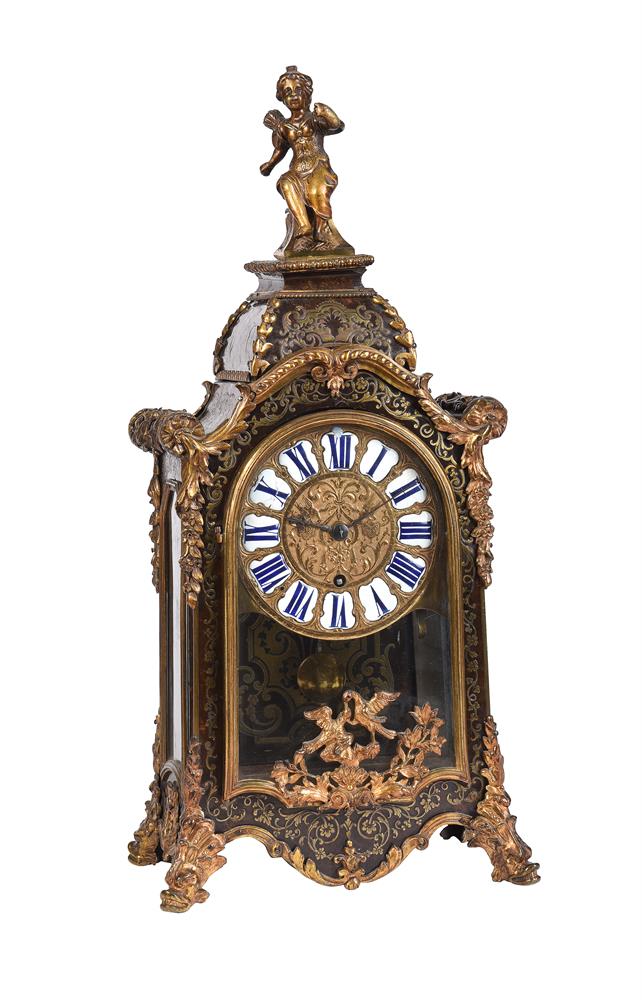
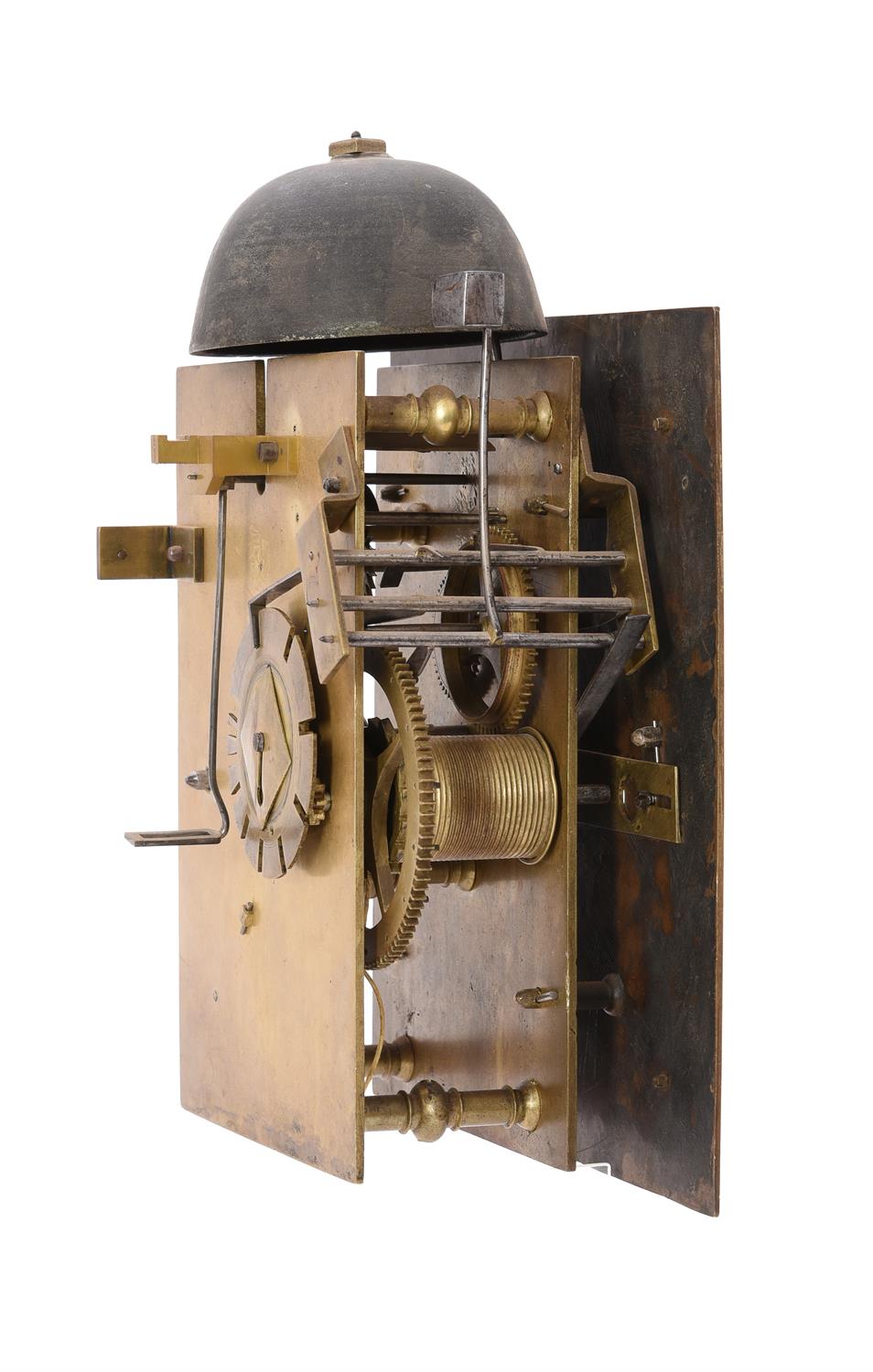
A very rare clockmaker s journeyman regulator or transit instrument movement Edward John Dent, London, mid 19 th century The six knopped pillar movement with arched plates measuring 8.625 by 5.25 inches containing a weight-driven three-wheel train incorporating Graham-type deadbeat escapement for regulation by a seconds pendulum and fitted with a pin to one of the crossings for operating the passing minute strike sounding on a bell mounted to the inside top left of the backplate, the frontplate silvered and engraved with integral dial with seconds ring incorporating Arabic five minutes and radial baton markers and with red-painted hand fitted directly onto the escapewheel arbor over signature Edward J. Dent, Strand LONDON across the centre and further minute dial with conforming numerals and batons with blued steel hand fitted directly on the greatwheel arbor. Edward John Dent was a talented horologist who at the age of 17 transferred his apprenticeship from the trade of tallow chandler to watchmaking under the charge of Edward Gaudin in 1807. By 1817 he had become well known as a watch and clockmaker receiving commissions from the Admiralty for a 'Standard Astronomical Clock' and pocket chronometers for the Colonial Office Africa Expedition. In 1830 Dent went into partnership with the renowned watch and chronometer maker John Roger Arnold which continued until 1840 when he left and set up business alone as E.J. Dent at 82 Strand, London, primarily making marine chronometers, watches and precision clocks. In 1843 the firm expanded taking on a second premises at 33 Cocksur Street, with the Strand premises moving down the road to number 61 by 1851. In 1852 Edward Dent successfully tendered to make the 'great clock' to be housed in Stephen's tower at the New Palace of Westminster. The clock was completed by 1859, apparently at a financial loss to the firm, however it ensured that Dent became a household name synonymous with fine clockmaking.Unfortunately Edward John Dent did not live to see the installation of the 'great clock' as he died in 1853. He was succeeded by his stepson Frederick Rippon Dent, who, in partnership with his brother Richard, continued to expand the business. By 1862 the firm had added 34 Cockspur Street and 34 & 35 Royal Exchange to their list of addresses and, although having seen natural passage of ownership over the intervening years, the business still continues to trade today as Dent & Co. The current lot is made to the design believed to have first been devised by the eminent horologist John Shelton in around 1770. Indeed four such timepieces were supplied to the Royal Observatory in Greenwich during the 1760 s and an example resides in the collection of the Museum of the History of Science, Oxford (Inventory number 46869). A very similar timepiece, this time by Ellicott and housed in a floor-standing case, is illustrated in Roberts, Derek English Precision Pendulum Clocks . Figs. 12-10 A,B and further example by John Holmes was sold at Bonhams, London sale of Fine Clocks 27 th June 2017 (lot 72) for £6,875. Traditionally such timepieces were thought to have been used in a workshop to assist in the regulation of watches where the rate can be checked by both reading the dial and listening for the passing strike sounding every minute. However it would appear that their primary purpose was to assist astronomers for timing the transit of celestial bodies. Indeed those supplied to The Royal Observatory were used by Neville Maskelyne for this purpose with one being described by him in a note written on 27 th April 1766. The relatively simple construction also made this type of regulator more suited to being transported hence they were often taken on expeditionary trips to be set-up in the field. Bearing these facts in mind it is most probable that the current lot was most likely made to be used for astronomical observations. It is also possible that it may have been taken on an expeditionary trip
A very rare clockmaker s journeyman regulator or transit instrument movement Edward John Dent, London, mid 19 th century The six knopped pillar movement with arched plates measuring 8.625 by 5.25 inches containing a weight-driven three-wheel train incorporating Graham-type deadbeat escapement for regulation by a seconds pendulum and fitted with a pin to one of the crossings for operating the passing minute strike sounding on a bell mounted to the inside top left of the backplate, the frontplate silvered and engraved with integral dial with seconds ring incorporating Arabic five minutes and radial baton markers and with red-painted hand fitted directly onto the escapewheel arbor over signature Edward J. Dent, Strand LONDON across the centre and further minute dial with conforming numerals and batons with blued steel hand fitted directly on the greatwheel arbor. Edward John Dent was a talented horologist who at the age of 17 transferred his apprenticeship from the trade of tallow chandler to watchmaking under the charge of Edward Gaudin in 1807. By 1817 he had become well known as a watch and clockmaker receiving commissions from the Admiralty for a 'Standard Astronomical Clock' and pocket chronometers for the Colonial Office Africa Expedition. In 1830 Dent went into partnership with the renowned watch and chronometer maker John Roger Arnold which continued until 1840 when he left and set up business alone as E.J. Dent at 82 Strand, London, primarily making marine chronometers, watches and precision clocks. In 1843 the firm expanded taking on a second premises at 33 Cocksur Street, with the Strand premises moving down the road to number 61 by 1851. In 1852 Edward Dent successfully tendered to make the 'great clock' to be housed in Stephen's tower at the New Palace of Westminster. The clock was completed by 1859, apparently at a financial loss to the firm, however it ensured that Dent became a household name synonymous with fine clockmaking.Unfortunately Edward John Dent did not live to see the installation of the 'great clock' as he died in 1853. He was succeeded by his stepson Frederick Rippon Dent, who, in partnership with his brother Richard, continued to expand the business. By 1862 the firm had added 34 Cockspur Street and 34 & 35 Royal Exchange to their list of addresses and, although having seen natural passage of ownership over the intervening years, the business still continues to trade today as Dent & Co. The current lot is made to the design believed to have first been devised by the eminent horologist John Shelton in around 1770. Indeed four such timepieces were supplied to the Royal Observatory in Greenwich during the 1760 s and an example resides in the collection of the Museum of the History of Science, Oxford (Inventory number 46869). A very similar timepiece, this time by Ellicott and housed in a floor-standing case, is illustrated in Roberts, Derek English Precision Pendulum Clocks . Figs. 12-10 A,B and further example by John Holmes was sold at Bonhams, London sale of Fine Clocks 27 th June 2017 (lot 72) for £6,875. Traditionally such timepieces were thought to have been used in a workshop to assist in the regulation of watches where the rate can be checked by both reading the dial and listening for the passing strike sounding every minute. However it would appear that their primary purpose was to assist astronomers for timing the transit of celestial bodies. Indeed those supplied to The Royal Observatory were used by Neville Maskelyne for this purpose with one being described by him in a note written on 27 th April 1766. The relatively simple construction also made this type of regulator more suited to being transported hence they were often taken on expeditionary trips to be set-up in the field. Bearing these facts in mind it is most probable that the current lot was most likely made to be used for astronomical observations. It is also possible that it may have been taken on an expeditionary trip














Try LotSearch and its premium features for 7 days - without any costs!
Be notified automatically about new items in upcoming auctions.
Create an alert